HodlX Guest Post Submit Your Post
Rising uncertainty in the global financial market sends increasing investors to safe-haven assets for defensive purposes. Crypto assets, other than precious metals and foreign currency products, have become a new alternative to protect against inflation and geopolitical risks.
Whether people expect things to go their way or not, Bitcoin, one of the most popular cryptocurrencies, has been playing a greater role to facilitate value exchange in the international financial market, despite its high volatility over the past 11 years. The market has developed a high demand for universally accessible spot markets to trade and derivatives markets to hedge risks.
Crypto exchange operators are, therefore, working on their plans of developing trading platforms to woo global investors. However, conservative parties mock crypto players by likening them to casinos due to futures, which are painted as the root of the past financial crises. Here it begs the question: is crypto derivatives trading a godsend or the Pandora’s box of the crypto industry?
Boon or Bane? History and Data Don’t Lie
The conservative camp has a long-term misunderstanding of financial derivatives as their nature gives rise to speculation with investors indirectly speculating on price changes to make a profit in derivatives trading. For example, George Soros, dubbed as a “financial crocodile”, is well known for his pound short to break the Bank of England. Also, a number of opportunistic Wall Street investors shorted property mortgage securities to get a big win during the subprime mortgage crisis in 2007.
Although those stories may have prompted many investors to back away from derivatives, the reality is not like this. Derivatives began in the form of clay tablets in Uruk during ancient Mesopotamia, when people had to offer food or perform worship service in temples on set dates. In the Roman empire, food futures were available for deploying macroeconomic controls. Multinational trades were frequent during the Age of Discovery, but the issue of commodity price volatility remained unsolved, owing to communication barriers, and could cause merchants to suffer a total loss after a shipment from one country or region to another. That was why commodity forward contracts were created by fleets to hedge against price volatility. After the 18th century, more developed stock exchanges introduced tightly defined sets of trading rules to help institutional investors manage exposure. Since then, this has attracted a greater participation of global investors in the market.
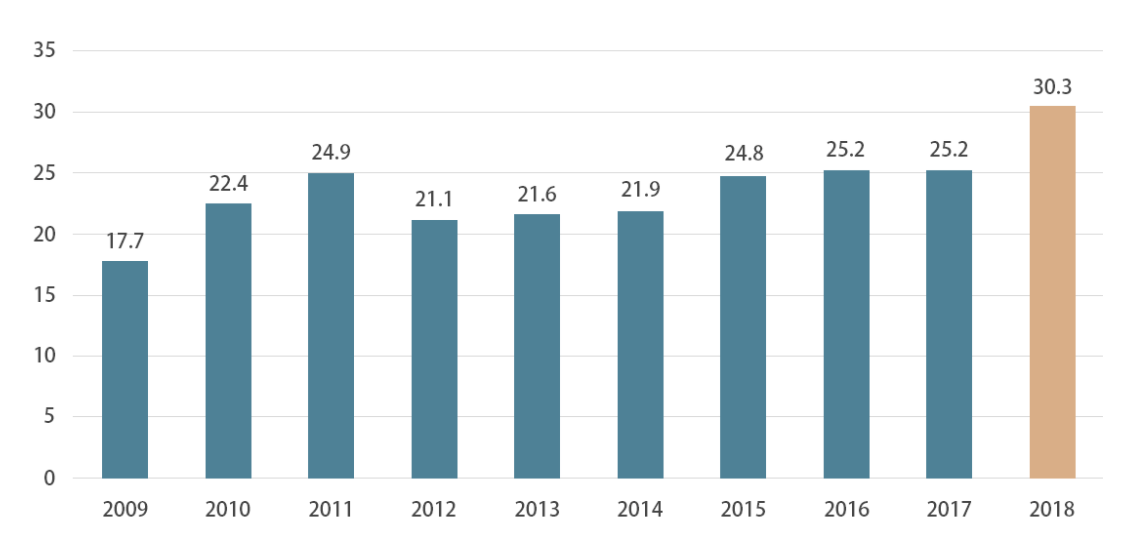
At present, the birth of futures contracts significantly helps achieve prompt delivery and maintain price stability. They do not only ensure orderly production of goods, but also offset volatility and other unfavorable conditions constraining enterprises from swiftly adjusting their production and marketing strategies. According to the latest data from the Futures Industry Association (FIA), the global futures and options trading volumes increased by 20.2% in 2018 to an all-time high of 30.28 billion contracts compared to 2017. The futures trading volume was up 15.6% to 17.15 billion contracts, and the options trading volume up 26.8% to 13.13 billion contracts. It is noteworthy that the growth of the global futures and options trading volumes in 2018 was the fastest since 2010.
Why are People Polarized on Derivatives?
Financial derivatives have their own value in controlling risk, reducing long-term price volatility and pricing assets fairly when we make reasonable use of them. But derivatives investors need to acquire enough knowledge and learn advanced strategies before trading so as to make good use of the instrument.
Many speculators fantasize a lot about getting rich overnight using derivatives for their highly leveraged nature. However, they tend to forget that the risk is also amplified while magnifying gains, and they overestimate their investment ability and psychological strength. Therefore, the most important approach for trading derivatives is to develop independent strategies first.
In this information era, many investors deliberately distort the truth of those “ big shorts” to exaggerate their successes while underplaying the risks involved. In 1992, Soros used his fund to build a huge short position in pounds sterling, bringing himself to the edge of a cliff. If the Bank of England had received foreign aid, he would have been put in danger. During the subprime mortgage crisis in 2007, the big shorts eventually took profits in a bullish real estate market with a strong will and good judgment after years of waiting on the sidelines. Every step to take advantage of a short-term trend is a bet, but this is rarely known by a lot of outsiders.
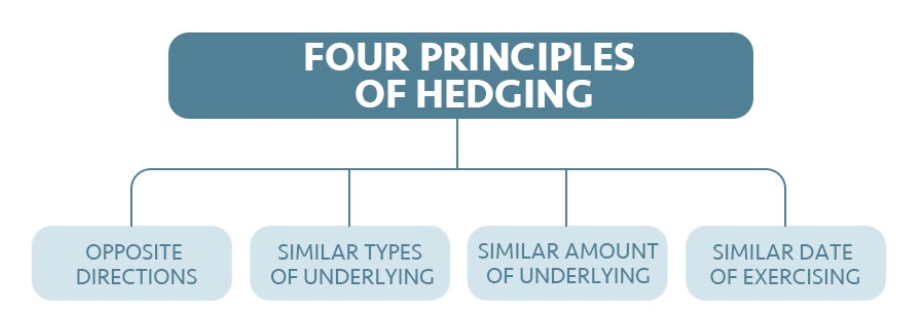
From a larger perspective, the crux of financial instability is the burst of asset bubbles. Derivatives are proved to act as a correction mechanism for investors and the market at critical moments, strengthening the overall stability of the financial industry after numerous trials and errors. Many global operators from key sectors, including oil and aviation, purchase inverse options to hedge the potential negative impacts on energy price and exchange rate fluctuations on inventory values. The explanation that derivatives trading is gambling is unconvincing because it helps support their healthy development.
Derivatives are the Godsend of the Crypto Asset Market
Crypto assets, which have become a new favorite of investors nowadays, are expanding at an unprecedented rate. The potential of this emerging market is attractive to many traders and investors. Nevertheless, the problem is that any investor may lose on the eve of victory amid volatility. The spot trading system was susceptible to negative rumors around the world resulting from market fear, uncertainty, and doubt, aka FUD. If crypto investors are unaware of the risks and lack of risk-hedging tools, it will be difficult for them to make returns in the long run.
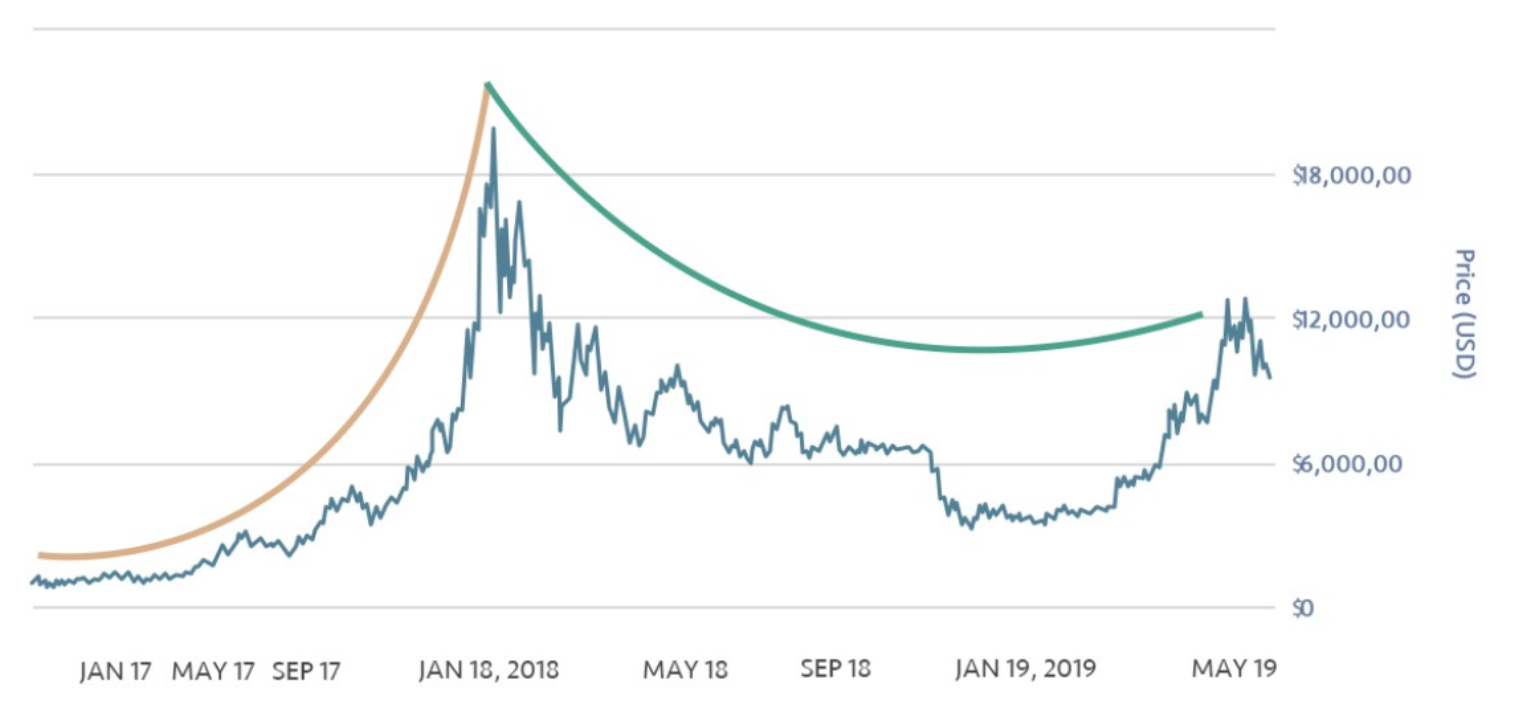
Both retail and institutional investors are facing the same issue. In 2012, the volatility of Bitcoin soared to as high as 94%, making both margin and spot traders suffer from unexpected losses. However, even if the media took this case out of context to regard crypto assets as speculative commodities, the long-term value of crypto assets has been evidently presented by the overall rise in their prices so far. The lesson for the industry is that investors need more instruments to withstand short-term volatility. After all, there are only a few who can lock their positions for a long while anyway.
Against this backdrop, the introduction of short-term hedging derivatives has come under the spotlight. In June 2013, the first Bitcoin futures contract was launched for shorting. Also, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) offered Bitcoin futures in 2017, and the volatility of BTC dropped significantly in a year’s time.
As a highly complicated investment tool, crypto derivatives are usually sought after by advanced and technical traders. The main value of them is for hedging exposure, reducing long-term price volatility and discovering reasonable prices of assets.
The maturing crypto derivatives market has apparently lowered the volatility of major cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, amid increasing trading volumes. The wider participation of institutional investors in the market has also led to a fairer market environment, paving a path for the healthy development of the crypto sector.
In the past, the lack of crypto derivatives greatly restricted the access of two groups of investors, namely miners and institutional investors, to the crypto market.
As we all know, miners need to bear the cost of a large number of mining rigs and electricity to operate a mining field. As a result, they only profit from the difference between the mining cost and the price of a cryptocurrency. In late 2018, Bitcoin dropped significantly from about $17,000 to $3,000, which directly hurt their livelihood. Even some sources said that miners had started to sell their mining machines by weight. Like airlines and oil companies, miners also need a risk-hedging tool to sustain their mining business. It’s a similar situation for institutional investors and crypto intermediaries.
As they hold a large amount of clients’ funds and hoard crypto assets strategically, they need such a financial instrument to deploy stabler investment strategies, taking into full account their clients’ interests and their own reputation.
Therefore, given the benefits derivatives can bring to both miners and institutional investors, they will undoubtedly become a booster that attracts new capital and brings impetus to the crypto market.
The volatility of the crypto market is far greater than that of the traditional ones. Crypto exchanges have tightened their risk management for derivatives products while their exploration of the derivatives market is still underway.
Young as the crypto industry is, we believe the rapid growth of crypto derivatives will be a cornerstone for the token economy and a blockchain-driven world.
This post originally appeared on OKEx Blog. Read more.
Disclaimer: This material should not be taken as the basis for making investment decisions, nor be construed as a recommendation to engage in investment transactions. Trading digital assets involve significant risk and can result in the loss of your invested capital. You should ensure that you fully understand the risk involved and take into consideration your level of experience, investment objectives and seek independent financial advice if necessary.
About OKEx
OKEx is a world-leading digital asset exchange headquartered in Malta, offering comprehensive digital assets trading services including token trading, futures trading, perpetual swap trading and index tracker to global traders with blockchain technology. Currently, the exchange offers over 400 token and futures trading pairs enabling users to optimize their strategies.
Follow us on Twitter.
Check our latest press material on Press Room.
Follow Us on Twitter Facebook Telegram