HodlX Guest Post Submit Your Post
The present cryptocurrency landscape may seem very crowded to outside observers, with analysts claiming that there are more than 5,000 cryptocurrencies and related projects in existence. However, the well-known industry leaders remain largely unaltered in their position in the market, with the likes of Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, EOS, Bitcoin Cash, etc. consistently featuring among the top 10 cryptocurrencies according to market cap.
The cryptocurrency market is still a thriving one, with trade volumes far exceeding that of a stock or CFD trading. However, not all cryptocurrencies are primarily used for money making or trading purposes. NEO, which is a project founded in 2014, is an open source, community-driven platform for building decentralized applications. Originally called “Antshares”, NEO has been breaking milestones and has won numerous accolades in less than five years. The company is co-founded by Da Hongfei and Erik Zhang.
As of May 17, 2019, NEO is trading at $13.43, with a market cap of $714,471,244. Its total circulating supply is 65,000,000 NEO at present.
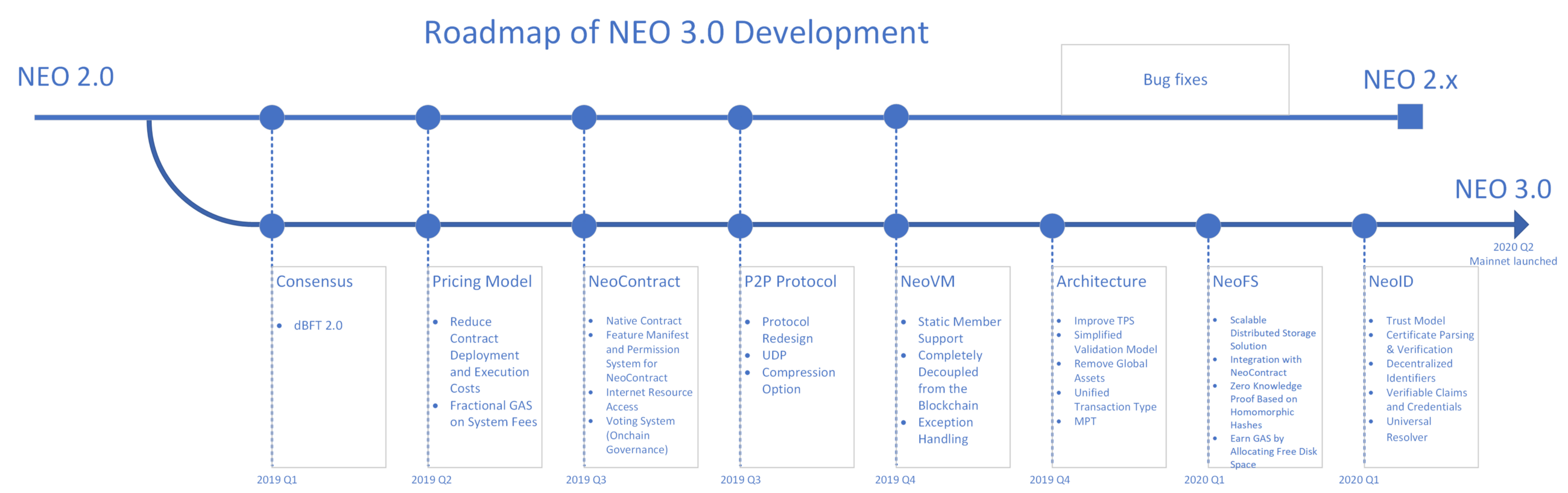
On April 29th, 2019, it was confirmed by the NEO team that they will launch a new version of their blockchain network, called NEO 3.0. The new chain was further explained by the co-founder and core developer of NEO, Erik Zhang, who described it as coming from a new genesis block. He further explained that the upgrade was necessary as the architectural improvements being implemented are not compatible with the current performance and stability of the existing NEO blockchain.
With the future in place for migrating decentralized apps along with data and transactions to the new 3.0 blockchain, NEO 3.0 looks to be the next giant step towards improving the entire NEO ecosystem, ushering in a new age of decentralized app development.
NEO 3.0 – Overview of Improvements
The NEO 3.0 blockchain is expected to be a robust blockchain implementation, enhancing the degree of stability and security, in addition to other improvements, especially the optimization of the existing smart contract system. All of this is targeted towards building a feature-packed infrastructure which can effectively deal with a diverse range of business application scenarios.
Thus, a multitude of new features has been introduced to address the inefficiencies of the previous NEO blockchain, which are explained in brief, below:
- New Pricing Model – The new pricing model aims to remove the obstacles currently faced during DApp usage and development. Neo and Gas are the native tokens on the platform, both of which are used extensively, with users being able to pay Gas which is being used for transaction fees as well as for smart contract execution. The steep cost associated with deploying and running smart contracts on the current blockchain discourages many users who are reluctant to take part in any development or usage using smart contracts. NEO aims to address these issues which plague the growth of DApp development on the NEO blockchain. The deployment and execution costs of smart contracts are significantly reduced, which results in the expansion of the application scenario of GAS. With this implementation, a credible project won’t be required to apply for grants from the NEO foundation with contract deployment costs.
- P2P Protocol and NEOVM – NEO 3.0 comes with a redesigned P2P protocol which enables compression options and adds support for the UDP communication protocol. This is aimed at significantly improving the TPS as well as the stability of the network. On the other hand, NEO has introduced a lightweight virtual machine for executing smart contracts called NEOVM. It is characterized by a fast start-up process, multiple high-level programming language support, and lower resource consumption. This virtual machine will be decoupled from the blockchain and will help in the easier implementation of native contracts among other benefits.
- Simple Architecture – The previous NEO blockchain offers just two methods for asset creation on the blockchain, with developers using either ‘Register Transaction’ or smart contracts. Global assets which are created by using Register Transaction are not integrated with smart contracts, which makes managing them a difficult task indeed.
Thus NEO 3.0 has discontinued support for global assets with all assets being created in smart contracts. - NeoFS – NEO 3.0 introduces NeoFS, which is a fully integrated, distributed, decentralized object storage platform, intended to be used by DApps for data storage and also as a Content Delivery Network. Rich Features include:
• scalable data placement method
• minimum data movement in case of node failure
• fine control over object location - NeoID – NeoID is newly introduced decentralized identity protocol by NEO, empowering users and organizations to have a better degree of control over their identities. It also delivers a higher degree of security and trust when it comes to the smart economy. It consists of three main components, namely, the Trust Model, Privacy Model, and Game Model.
- Internet Resource Access – NEO 3.0 introduces a built-in oracle implementation, allowing smart contracts to easily access internet resources during execution. This feature will enable users to develop both advanced and scenarios-specific on the blockchain, allowing DApps to rely more on external data.
- dBFT 2.0 – dBFT 2.0 stands for Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance, which is a consensus mechanism designed for blockchain networks. A vote selects a set of consensus nodes, which in turn generate and validate blocks together. It provides a single block finality, disallowing any forks or reversal of transactions on the blockchain. It also contains an added recovery mechanism for instances such as network failures or node failures.
How NEO 3.0 Aims to Solve Problems in The NEO Blockchain
With the release of NEO 3.0, NEO is ready to take a massive step forward towards their aim of supporting enterprise level commercial applications via the blockchain. The above features are aimed at solving some of the lingering problems plaguing the previous blockchain. These are mentioned in brief below.
- Improvements for Financial Applications – The previous NEO blockchain could be forked and transactions could be reversed, which is not a good feature to have when it comes to developing financial transactions. With the addition of the new Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus mechanism, transactions are now irreversible, which makes it more suited for building secure financial applications.
- Solving Inconsistency Issues Between Nodes – With the implementation of NEO’s new built-in oracle, the previous inconsistencies faced between nodes while accessing internet resources are thus largely resolved.
- New Virtual Machine – The NeoVM, which is a lightweight virtual machine to execute smart contracts has immense benefits to offer to the blockchain. This includes the easier implementation of native contracts on the blockchain, usage in applications outside the blockchain, easy integration into any IDE and easier debugging among others.
- Removing the Requirement of Global Assets – With the introduction of a much simpler architecture, NEO 3.0 does not require global assets anymore. By removing global assets, users can now unify all transaction types, which is vastly different from the previous NEO blockchain which had nine different types of transactions.
- Faster Transaction Verifications – NEO 3.0 has made improvements to their validation model, which results in faster transaction verification speeds, allowing validation to be performed concurrently.
- Creating Private Distributed Storage Systems – With NeoFS, it is now possible to create private distributed storage systems for small to medium-sized enterprises, which require servers or data centers for storing large amounts of unstructured data.
- Solving Scalability Issues – With the introduction of NeoFS, storage can now be done on data nodes instead of the blockchain ledger. This has the potential to not only decrease the cost of smart contract deployment. Additionally, the introduction of NeoFS can store old block data instead of full nodes, which in turn increases the scalability of the NEO.
- Divisibility of NEO – It was impossible to buy or sell a fraction of NEO on the previous blockchain. NEO 3.0 enables the transactions of fractions of cryptocurrencies including both NEO and GAS.
- Zero-Knowledge Data Validation – With the inclusion of the NeoFS system, a new “zero-knowledge data validation method” has been introduced, based on ‘homophormic’ hashing. This, in turn, minimizes data transfers, which helps in maintaining network scalability. Computational costs on storage nodes and validation nodes are minimized significantly, ensuring a large number of parallel interactions.
- Dealing with complex application scenarios – With the removal of global assets in the NEO 3.0 blockchain, related transactions which deal with intricate application situations will be removed and replaced with the services promised in smart contracts. This makes it possible to reduce the type of transactions from several to only one.
- Performance of the base layer – The new architectural changes made to NEO 3.0 substantially increase the performance of its base layer by many folds. These features, however, can lead to incompatibility with the older NEO 2.x blockchain and plans are thus delayed until all NEO 2.x compatible features are developed.
The Migration Plan
The ultimate plan of migration to NEO 3.0 applies to all DApps as well as users. Although the full details of the migration are still under development to create a comprehensive plan, NEO has indicated some primary principles which will be applied to this migration, no matter what.
- The migration is slated to be simulated in the TestNet to ensure a smooth transition.
- All data and transaction records on the old NEO 2.x blockchain are permanently retained
- The NEO Foundation will reimburse any costs incurred during migration, including for contract redeployment as well as testing.
- Comprehensive technical support will be provided by the NGD team for DApp migration. The NGD team is dedicated to the research and development of the NEO ecosystem, with offices in Shanghai and Seattle.
- Users on exchanges will not be affected.
- To activate the new NEO 3.0 tokens, token holders are required to swap the old tokens.
- An early adopter incentive plan is introduced to encourage users and DApps to migrate. The full details of this plan will be released eventually.
Advantages of Native Contracts on NEO 3.0
Native contracts are a feature of the new NeoContract component in the NEO 3.0 blockchain, developed and merged into the master brand. It carries over features from the previous contracts, such as Gas distribution, consensus node elections and voting,
Native contracts offer a host of new features, which are mentioned in brief below.
- New Feature for GAS – Unlike in the previous NEO blockchain where three separate steps were required to claim generated GAS, native contracts allow GAS to be collected automatically by the token holder, every time he or she sends or receives a transfer in NEO.
- Adding Economic Models – With NEO 3.0, developers can easily add economic models to their DApp projects, combined with NEO and GAS.
- Exchange generated GAS – Previously Gas generated through NEO deposits by users on an exchange was very difficult to claim and involved complicated steps. NEO 3.0 makes this process simple.
- NEO and GAS – In NEO 3.0, both NEO and GAS become smart contracts, with their system functionality also carried over. As a result, users can easily integrate different contracts. Also, NEO and GAS contracts are compatible with the NEP-5 standard, allowing native assets to be directly managed by any wallet or client.
Closing Thoughts
The release of NEO 3.0 has been touted as the cornerstone of the efforts of the development team which has tirelessly worked towards building a robust blockchain network with an optimized smart contract system. The NEO team also recognizes the increased role of governance in today’s blockchain world. With plans to collaborate with experts from varied industries such as academia and finance, various governance mechanisms are expected to emerge in the coming months.
NEO at present has 176 trading markets across exchanges around the world and is ranked 20th according to CoinMarketCap. With the NEO token being traded on big exchanges such as Binance, Bitmart, DigiAFinex, CoinMEx, LBank and OKEx, the NEO team is well on the way to exploring various governance mechanisms such as futarchy, liquid democracy and tightly interfaced economic models.
Yousef Faisal stumbled across cryptocurrencies, specifically Ripple, back in 2017. He got involved with trading some altcoins and has been hooked ever since. For more information on his learning experience and trades, please visit his blog.
Follow Us on Twitter Facebook Telegram